First, the size and granularity analysis
Particle size is a measure of the particle size, which is usually expressed as "diameter". The minerals processed during the beneficiation process are mixtures of various sizes of ore particles. The mineral grain mixture is divided into several levels according to the particle size, and these levels are called the grain size. The relative content of each grain size of the ore particles is called the particle size composition. The measurement of the particle size composition or particle size distribution of the ore material directly or indirectly to understand the particle size characteristics of the mineral material is called particle size detection.
Size detection is a very important job, are often used in many industrial sectors such as cement industry, chemical industry, metallurgical industry, coal industry, ceramic industry, agricultural soils and food processing sectors, there is a particle size measurement The problem is even more indispensable in the beneficiation process. Raw ore, intermediate products, concentrates and tailings often require particle size testing.
The method of expressing the particle size can be divided into three types, namely, the equivalent spherical diameter, the equivalent circle diameter and the statistical diameter, as shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Figure 1.
Table 1 Â Equivalent sphere diameter
name | Equivalent diameter of the ball | symbol |
Volume diameter 2. Surface area diameter 3. Blocked diameter 4. Specific surface diameter 5. Free settlement diameter 6. Stokes diameter 7. Screening diameter | The particles have the same volume Particles have the same surface area When moving at the same speed in the same fluid, the particles are subject to the same resistance Particles have the same specific surface In the same fluid, the particles have the same free settling velocity In R εd <0.2 (Stokes range), the particles have the same free settling velocity Particles pass through the same mesh | X v X s X d X st X f X st |
Table 2 Â Equivalent circle diameter classification
name | Equivalent nature of the circle | symbol |
1. Projection area diameter 2. Projection area diameter 8. circumference diameter | The projected area of ​​the stable position of the particles is equal The projected area of ​​the random position of the particles is equal The contour of the particle projection is equal | X a X p X e |
For regular shaped particles, the surface area is proportional to the square of the linear dimension. The volume is proportional to the cube of the linear dimension.
Figure 1 Â Statistical diameter diagram [next]
x F - the Feret diameter, which is the distance between two tangent lines perpendicular to the fixed direction on the opposite side of the particle;
x m — Marttn diameter, which is the length of a line segment parallel to the fixed direction and dividing the projected area of ​​the grain into two equal parts;
x CH — the maximum chord diameter, which is the longest linear dimension of the granule;
x cm — the smallest chord diameter, the shortest linear dimension of the granule
Particle size distribution Particles of mineral processing products are rarely narrow-scale, and are not uniform. In most cases, they are a continuous distribution of a wide level, that is, the maximum is close to zero by d. Particle size detection therefore includes both the detection of individual particles and, more importantly, the detection of continuous populations. It is called "granularity analysis".
The particle size distribution of the granular material can be expressed in two ways, namely frequency distribution and cumulative distribution, as shown in FIG.
It can be seen from the frequency curve of Fig. 2 that the area under the curve is the total yield of each grain level, that is, 100%, and the small area (shaded part in the figure) composed of any x~(x+ds) is x~( x+ds) The yield of the grain size, whose approximate value is Æ’(x)dx, therefore, (see the cumulative curve in the figure), that is, if the frequency distribution curve function is known as Æ’(x), the cumulative distribution curve can be known. And actually. The cumulative curve is always smooth, and the frequency curve is not easy to be smooth, so the frequency distribution of the particles must be obtained by the differential method.
which is
Æ’(x)=dF(x)/dx
(1)
Both Æ’(x) and F(x) are functions that characterize the particle size composition of the material. Since the particle size characteristics of the beneficiation product have certain regularity, it is possible to try to fit the particle size distribution of the product to some analytic function.
Figure 2 Â Frequency distribution and cumulative distribution
A—frequency distribution; b—cumulative distribution [next]
Second, the settlement balance
The particle size distribution analyzer produced by Shimadzu, Japan is based on the Stokes method (Stokes diameter), based on the relationship between particle size and sedimentation velocity when particles are settled in a suitable liquid medium, and the particle is determined. Particle size distribution. The density change of the suspension is measured by a precision balance (specific gravity balance method) while indicating and recording, whereby the particle size distribution of the particles can be directly displayed.
1. Working principle
(1) Principle of settlement method
When the particles settle in a liquid medium, its settling velocity (end velocity) is expressed by the following Stokes formula
H 2g(Ïf-Ïs)
v=---=-------------
T gη
(2)
Where υ—settling velocity, cm/s;
H—sedimentation distance, cm;
T—settling time, s;
G—gravity acceleration, cm/s 2 ;
Ï s — liquid medium density, g/cm 3 ;
Ï f — the density of the powder, g/cm 3 ;
Η—the viscosity of the liquid medium, g/cm·s;
R—the radius of the particle, cm.
Therefore, if the time T at which the particles settle the distance H is known, the radius r of the particles can be obtained.
If the particles do not interfere with each other, this formula can be used for the sedimentation of the particle group. Therefore, the particle size and particle size distribution can also be determined.
(2) Principle of the instrument
The instrument uses the formula (2) to determine the particle size distribution of the powder from the relationship between H and r containing the parameter T.
From equation (2)
(3)
If T=constant
(4)
Here
(5)
It is known from the formula (4) that when the particle groups having the same density and different radii (r 1 , r 2 ..., r n ) are uniformly dispersed in the medium, they are left for some time (for example, T=T 1 ) and have a radius of r 1 . The particles of r 2 , ... r n settle to a corresponding distance.
In such liquid media (i.e., suspensions), there are different density differences corresponding to different settling distances, which is the signal accumulation of the powder particle size distribution. Therefore, the particle size distribution of the particles can be obtained by indicating and measuring the difference in density.
Figures 3a, b, c, d show the relationship between the settling distance H and the concentration of the suspension.
2. Structure
The instrument structure is divided into three parts. The block diagram of the instrument is shown in Figure 4 and is briefly described below.
(1) Density difference measurement system
This part consists of a balance and a density difference measuring amplifier. In a liquid medium, the change in density is detected as a difference in density (ie, only the density of the liquid medium and the density of the dispersed sample suspension are compared by two sinkers). ) and zoom in. [next]
Figure 3 Â Relationship between settlement distance H and suspension concentration
aT=0; bT=T 1 ; cT=T 2 ;dT= ∞
Figure 4 Â Full instrument block diagram
A block diagram of this part is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Â Density difference measurement system block diagram
Container Nitrogen Generator
Outdoor Container all-in-one PSA Nitrogen Plant is the compact Nitrogen Generator designed for customers who need
all-in-one solution. For some customers, their site area is limited, and
they prefer one container nitrogen generator every part inculded. Some
cusotmers need the nitrogen generator have low noise, rain proof, this
container type nitrogen plant is the ideal solution.
Air Compressor suction
air from atmosphere,then the compressed air enters one air treatment
part to get rid of dust,water, dust,etc, achieving clean and dry
compressed air. This air treatment part mainly consists of three
filters, one Refrigerant Dryer and one activated carbon oil remover.
After treatment, the compressed air enters one air tank to make air
stable. Then the compressed air enters PSA nitrogen/oxygen separator.
After passing through this nitrogen/oxygen separator part, nitrogen is
collected. The produced nitrogen enters one nitrogen buffer tank. At the
outlet of nitrogen buffer tank, stable and qualified nitrogen is sent
to using point.
Below is a container nitrogen generator with 98% purity, 1200 Nm3/hr flow rate.
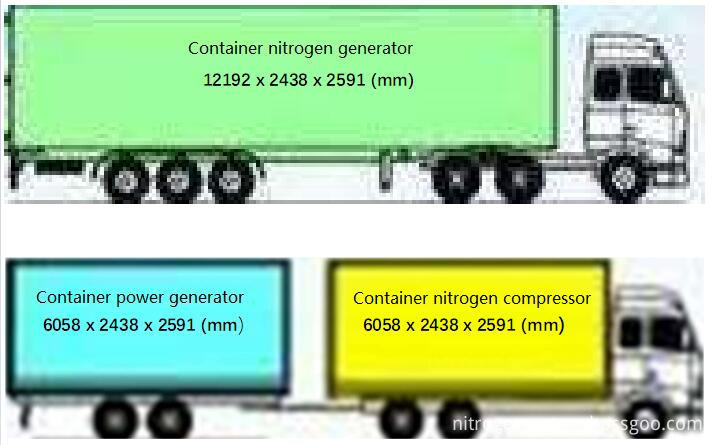
Container nitrogen generator technical specification
Flow rate: 5-2000 Nm3/hr
Purity: 95-99.999%
Outlet perssure: 5-200 bars(72.5-2900 psi)
Container Nitrogen Generator,Container Psa Nitrogen Generator,Containerized Nitrogen N2 Generator,Container Nitrogen Gas Generator
Shandong Gamma Gas Engineering Co. Ltd. , https://www.gammagases.com








